From representing to modelling knowledge: proposing a two-step training for excellence in concept mapping
Joana G. Aguiar, Paulo R. M. Correia
Resumo
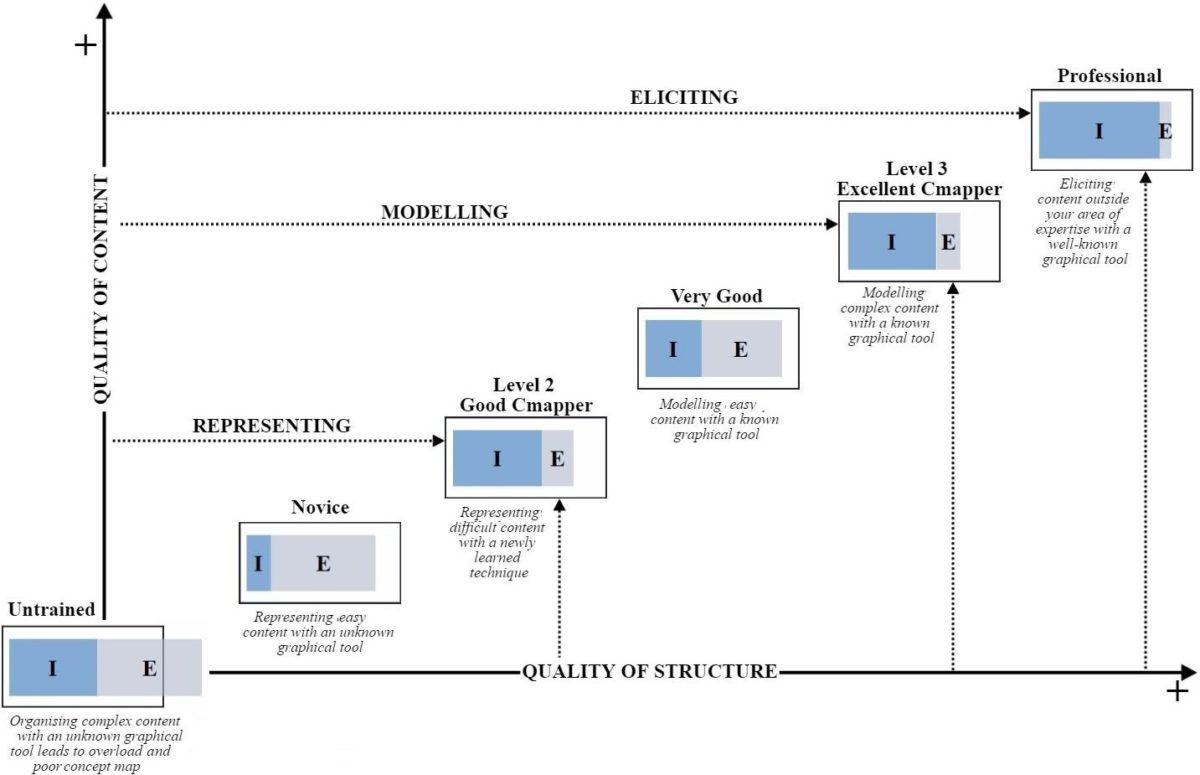
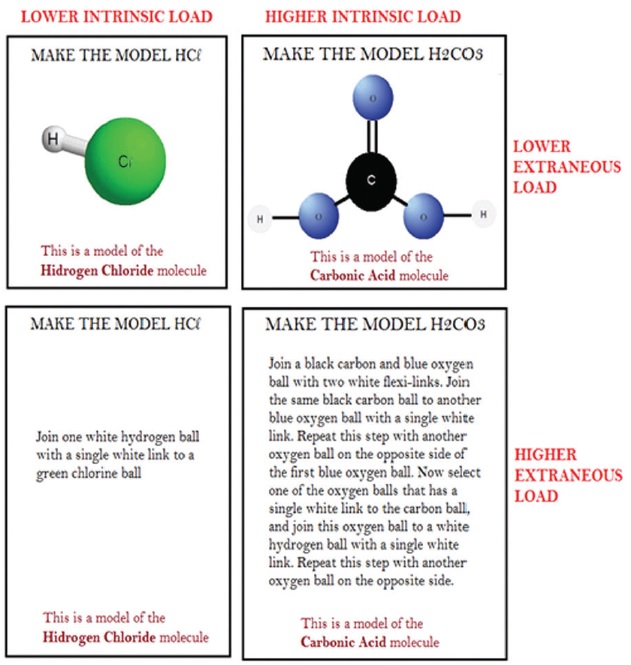
Training users in the concept mapping technique is critical for ensuring a high-quality concept map in terms of graphical structure and content accuracy. However, assessing excellence in concept mapping through structural and content features is a complex task. This paper proposes a two-step sequential training in concept mapping. The first step requires the fulfilment of low-order cognitive objectives (remember, understand and apply) to facilitate novices’ development into good Cmappers by honing their knowledge representation skills. The second step requires the fulfilment of high-order cognitive objectives (analyse, evaluate and create) to grow good Cmappers into excellent ones through the development of knowledge modelling skills. Based on Bloom’s revised taxonomy and cognitive load theory, this paper presents theoretical accounts to (1) identify the criteria distinguishing good and excellent concept maps, (2) inform instructional tasks for concept map elaboration and (3) propose a prototype for training users on concept mapping combining online and face-to-face activities. The proposed training application and the institutional certification are the next steps for the mature use of concept maps for educational as well as business purposes.
Leia o artigo completo
Clique aqui para acessar o texto completo.